Ever wondered how your phone magically connects to the right network, whether you’re at home or halfway across the world? This seamless global connectivity isn’t magic—it’s a highly organized system built on a universal language of codes. The two most important identifiers in this system are the Mobile Country Code (MCC) and the Mobile Network Code (MNC). Understanding these codes is key to understanding how our entire mobile ecosystem functions.
This comprehensive guide is your definitive resource for everything related to the mobile country code and the mobile network code. We will break down exactly what these codes are, how they work together, and why they are essential for everything from international roaming to app development. You will also find a detailed mobile network code list for the USA, helping you identify specific carriers like US Cellular and others. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of the invisible architecture that powers our connected world.
The Core Explanation: What Are MCC and MNC?
At the very heart of global mobile communications is a standardized system that gives every network a unique address. Think of it like a postal system: the MCC is the country, and the MNC is the specific street address of the mobile carrier. Together, they form a unique network code that allows any device to identify any network, anywhere on Earth.
What is a Mobile Country Code (MCC)?
So, what is a mobile country code? An MCC is a three-digit code established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) to identify a specific country. Every single mobile operator within a country shares the same MCC mobile country code. This is the first piece of information a network uses to identify a subscriber’s home country.
The first digit of the MCC country code even corresponds to a specific continent, making the system geographically organized:
- 2: Europe
- 3: North America and the Caribbean
- 4: Asia and the Middle East
- 5: Australia and Oceania
- 6: Africa
- 7: South and Central America
For example, the United States mobile country code range is 310-316 (you will often see the mobile country code 310 used). The mobile country code for the UK is 234. This simple code is the foundation of global network identification.
What is a Mobile Network Code (MNC)?
Now, what is a mobile network code? The MNC is a two- or three-digit code that identifies a specific mobile operator code or mobile carrier code within a country. While everyone in the USA shares the mobile country code 310, AT&T, Verizon, and T-Mobile each have their own unique MNCs. The combination of MCC and MNC creates a globally unique network code number.
In North America, MNCs are typically three digits, whereas in Europe they are often two digits. This complete identifier is what allows your phone to distinguish between different networks.
How They Work Together: The PLMN
The MCC and MNC are combined to form a Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) code, also known as a Home Network Identity (HNI). When your phone scans for signals, it’s looking for these PLMN codes. For instance, a major T-Mobile US PLMN is 310-260. This tells your device it’s seeing the T-Mobile network within the United States. This elegant, hierarchical system is what enables the massive scale and reliability of global mobile communications.
The Deep Dive: How Codes Identify You (The IMSI)
While the PLMN identifies the network, a different code identifies you, the subscriber. This is the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), a unique 14- or 15-digit number stored on your SIM card. The IMSI is your digital fingerprint on the mobile network.
Its structure is a clear hierarchy:
IMSI=MCC+MNC+MSIN
- MCC + MNC: The first 5-6 digits identify your home country and network operator.
- MSIN (Mobile Subscriber Identification Number): The remaining digits are a unique number assigned by your carrier to identify your specific account.
For example, a US Cricket IMSI code would start with the MCC for the United States (like 310) and the MNC for Cricket, followed by the unique MSIN for that user. Because the IMSI is sensitive, your device is assigned a temporary ID (TMSI) after its first connection to protect your privacy over the airwaves.
It’s easy to confuse the different acronyms in telecom. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Identifier | What it Identifies | Where it’s Found | Can it Change? |
| IMSI | The Subscriber Account | SIM Card / eSIM | Yes (with a new SIM) |
| IMEI | The Physical Phone | Device Hardware | No (Permanent) |
| ICCID | The Physical SIM Card | SIM Card Chip | Yes (with a new SIM) |
Clearing Up Confusion: Mobile Codes vs. Phone Country Codes
Many people confuse the mobile country code mcc with the telephone country codes used for dialing. They are completely different.
- Mobile Country Code (MCC): Used by network equipment to identify a subscriber’s home network for data routing and authentication. This is machine-to-machine communication.
- Phone Country Codes (e.g., +1): Used by people to place international calls. The phone country codes for the USA is +1, while the US mobile country code is 310. They serve entirely different purposes.
| Identifier Type | Code | Purpose | Example |
| Mobile Country Code | 310 | Identifies the US for network authentication. | Your SIM card’s IMSI starts with 310. |
| Telephone Country Code | +1 | Prefixes a phone number for placing a call. | You dial +1 to call the United States. |
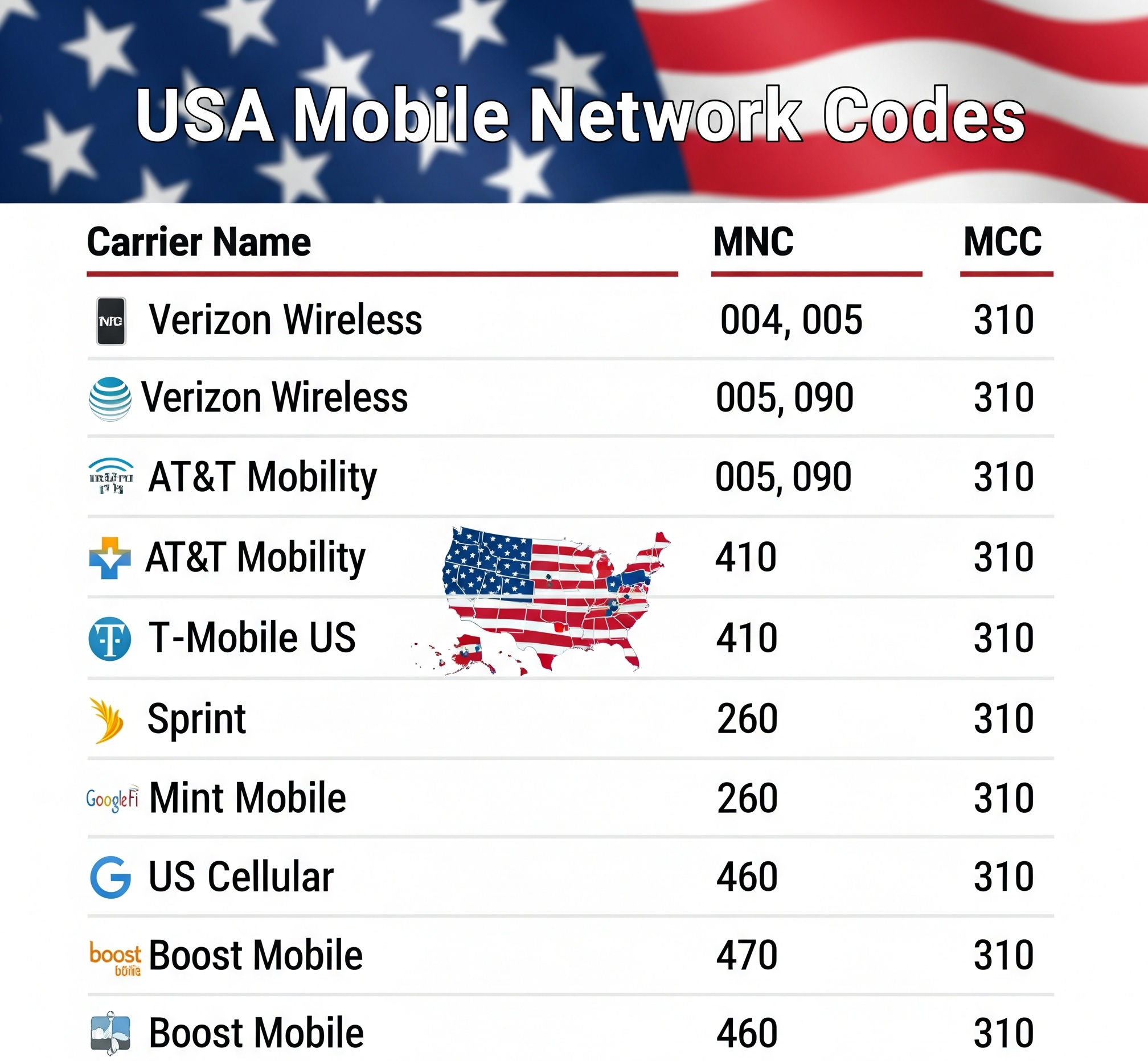
The Complete US Mobile Network Code List
The United States has one of the most complex mobile markets, with a wide range of MCCs (310-316) and hundreds of MNCs assigned to national carriers, regional operators, and even private companies like SpaceX. This mobile network codes list provides a look at some of the most important network codes in the mobile country code for USA.
| MCC | MNC | Operator / Brand | Notes |
| Major Carriers | |||
| 310 | 410 | AT&T Mobility | Primary modern AT&T MNC. |
| 311 | 480 | Verizon Wireless | Primary LTE/5G MNC. |
| 310 | 260 | T-Mobile US | Primary T-Mobile MNC. |
| 313 | 340 | Dish Network | New nationwide 5G network. |
| US Cellular MCC MNC | |||
| 310 | 940 | U.S. Cellular | The US Cellular MCC and US Cellular MNC for this major regional carrier. |
| Other Notable Operators | |||
| 313 | 100 | AT&T FirstNet | Dedicated public safety network. |
| 310 | 950 | AT&T Mobility / FirstNet | Another code used by AT&T. |
| 310 | 310 | T-Mobile US | Formerly MetroPCS. |
| 310 | 012 | Verizon Wireless | Legacy Verizon network. |
| 314 | 850 | SpaceX / Starlink | For emerging satellite-to-phone services. |
| 312 | 580 | Google, LLC | For experimental and research use. |
This list of mobile country codes and network codes is constantly evolving as the industry changes. For example, the UK mobile network codes (or uk network code) are similarly extensive, reflecting the diverse market there under the uk mobile country code 234.
Practical & Actionable Advice: Real-World Applications
These mobile network codes are not just for network engineers; they have practical applications that affect everyday users, developers, and businesses.
- International Roaming: When you travel, your phone scans for local PLMN codes and compares them to a preferred list on your SIM card. The visited network reads your IMSI, sees your home MCC/MNC, and contacts your home carrier to authorize service and billing.
- IoT & Device Configuration: Developers of Internet of Things (IoT) devices use MCC/MNC lists to program devices to connect to specific networks, ensuring reliability and managing costs for large-scale deployments.
- Mobile App Development: App developers can use the MCC/MNC to create context-aware experiences. An app can check the SIM’s home network (getSimOperator()) to verify a user’s country for security, or check the currently connected network (getNetworkOperator()) to apply regional content restrictions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is a mobile country code used for? A: A mobile country code (MCC) is a 3-digit number that uniquely identifies a country in the global mobile network system. It’s the first part of a network’s unique address and is used by mobile devices and infrastructure to determine a subscriber’s home country for authentication and roaming.
Q2: What is the difference between MCC and MNC? A: The MCC identifies the country, while the Mobile Network Code (MNC) identifies the specific mobile operator within that country. For example, the America mobile country code is 310, and an MNC of 410 specifies the AT&T network. You need both to identify a network.
Q3: Can a single mobile operator have more than one network code? A: Yes, it’s very common. Large carriers often have multiple MNCs due to mergers (acquiring other companies’ codes), for different network technologies (e.g., 4G vs. 5G), or for specialized services like a dedicated public safety network.
Q4: Do virtual operators (MVNOs) like Mint Mobile have their own MNC? A: Most do not. They typically use the MCC and MNC of their host network (for example, T-Mobile). However, some larger, more established MVNOs are assigned their own MNC to have greater control over their services and SIM cards.
Q5: Where can I find a complete mobile country code list? A: The most authoritative source is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which maintains the official global registry. Several reputable online resources also compile and publish an up-to-date mcc mobile country code list and mobile network code list.
Conclusion
The Mobile Country Code (MCC) and Mobile Network Code (MNC) are the unsung heroes of our connected age. This invisible system of network codes works tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure our devices can connect reliably and securely, no matter where we are. From the mobile country code for the United States to the specific US Cellular network code, each identifier plays a critical role in a global symphony of communication.
لا تعليق